The Madrasa education system is a traditional form of Islamic education that focuses on religious as well as some secular subjects. The word Madrasa literally means “a place of study” in Arabic. These institutions have been a cornerstone of learning in many Muslim communities for centuries.
What Is Madrasa Education System?
The word “Madrasa” literally means school or place of learning in Arabic. So, before you imagine something mysterious, know that a madrasa is simply an educational institution like any other school but with a focus on religious and moral education.
In the Madrasa Education System, students study Islamic theology, Arabic, the Quran, Hadith, and sometimes modern subjects like science, math, and English. Over time, madrasa meaning in English became “Islamic school,” but in practice, it often functions as a community learning center, especially in rural or underprivileged areas.
So, if you’re thinking “What is a madrasa education system?” It’s a blend of faith, discipline, and traditional scholarship, all wrapped in a humble classroom environment.
A Brief History of Madrasa Education
The history of madrasa education in Islam stretches back to the 10th century. The famous Al-Azhar University in Cairo, for example, started as a madrasa and is still a global symbol of Islamic learning.
In India, the story began during the Delhi Sultanate and blossomed under the Mughals. Madrasas like Darul Uloom Deoband became intellectual hubs, producing scholars who shaped both religion and politics.
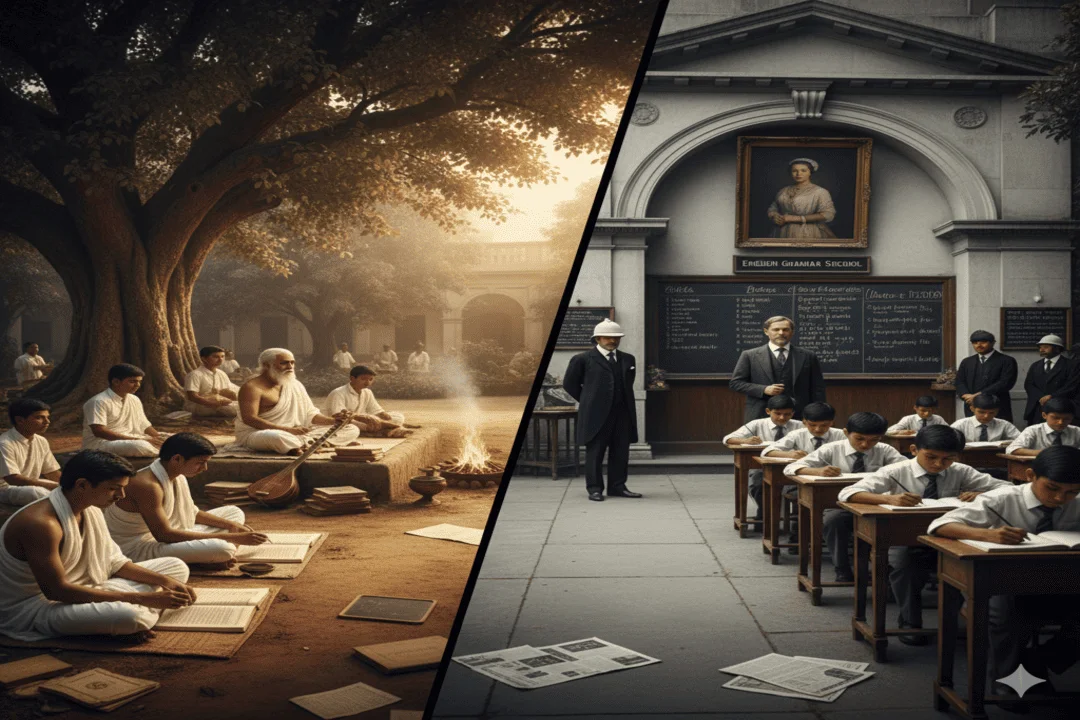
Under British rule, madrasa education in India faced big changes. English-medium schools and modern subjects gained prominence, while traditional madrasas were seen as “old school.” Ironically, today many are modernizing faster than government schools!
After independence, India continued to support these institutions through various acts and boards, like the Uttar Pradesh Madrasa Education Act, ensuring recognition and funding for thousands of madrasas.
Structure, Curriculum and Types of Madrasas
The structure of madrasa education may surprise you it’s quite organized! There are generally four main stages:
- Maktab – the elementary level for Quran recitation.
- Madrasa (basic level) – where theology, Arabic grammar and Islamic law are introduced.
- Alim/Fazil/Kamil levels – equivalent to higher secondary and college education in the madrasa framework.
The madrasa curriculum, traditionally known as Dars-e-Nizami, covers Islamic jurisprudence (Fiqh), Arabic literature, and logic. But modern reforms are adding new flavors think computers, environmental studies and even robotics!
There are also types of madrasa in India some focus purely on religion, while others mix secular and religious subjects. The goal is to help students gain both spiritual wisdom and employable skills.
If you compare the madrasa vs modern education systems, the difference mainly lies in focus: one nurtures faith and identity, the other targets jobs and technology. Ideally, we need both the heart of one and the skills of the other.
Current Status of Madrasa Education in India
So, how many madrasa in India today? Estimates say over 30,000 registered madrasas, and many unregistered ones too. States like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal host the largest numbers.
The madrasa board of India and various state boards oversee recognition and examinations. There’s also a central madrasa board proposal to bring standardization across states, though it’s still under debate.
Government schemes like SPQEM (Scheme for Providing Quality Education in Madrasas) and SPEMM aim to modernize the system funding teachers, training programs and digital education tools. But implementation is patchy.
In some areas, students still face challenges entering mainstream universities, even after completing their madrasa education in India. Efforts are on to bridge this gap and ensure equivalence with other school boards.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Madrasa Education
Let’s be honest every system has its pluses and minuses.
Advantages of madrasa education:
Preserves culture and religious identity.
Offers free or low-cost education to poor communities.
Promotes moral values and discipline.
Provides safe spaces for community interaction.
Disadvantages:
Outdated curriculum in some regions.
Limited job opportunities due to lack of modern subjects.
Poor infrastructure and teacher training.
Gender imbalance fewer girls’ madrasas in rural areas.
That’s why discussions about madrasa education advantages and disadvantages are essential for reforming without erasing tradition.
Challenges in the Madrasa Education System
According to experts and reports like Drishti IAS and ClearIAS, the biggest challenges in madrasa education today are:
- Lack of standardization each board follows its own structure.
- Low funding and outdated teaching methods.
- Poor infrastructure, especially in remote areas.
- Difficulty integrating with modern job markets.
- Perception issues stereotypes that often overshadow real achievements.
Some madrasas also face legal or recognition hurdles under acts like the Right to Education (RTE) and policies differ across states. That’s why reform efforts are so important.
Reforms and Modernization Programs
Reform doesn’t mean replacing tradition, it means upgrading it.
The madrasa modernization program by the Indian government focuses on adding science, mathematics and computer literacy to traditional subjects. It also encourages English teaching, vocational skills, and teacher training.
Modernized madrasas under SPQEM are blending deen (religion) with duniya (worldly knowledge). Many even run community development programs.
However, successful reform depends on cooperation between governments, scholars, and local communities. And yes, we still need better funding chalkboards and centuries-old libraries don’t buy themselves!
Madrasa vs Modern Education
When comparing madrasa vs modern education, think of it as comparing “Google Classroom” with “Gurukul 2.0.”
While modern schools emphasize digital literacy and career readiness, madrasas focus on spiritual development, ethics and community service. The ideal education system would merge both creating students who are not only employable but also empathetic and morally grounded.
This brings us to another classic debate: the difference between madrasa and Gurukul. Both are ancient systems, deeply rooted in culture and community, and both emphasize values and discipline. The Gurukul Education System trained spiritual and social leaders in India, while madrasas produced theologians and scholars two sides of the same traditional coin.
Importance and Role of Madrasa Education
Despite criticisms, the role of madrasa in Muslim education cannot be understated. For centuries, these institutions have:
- Preserved languages like Arabic, Urdu, and Persian.
- Provided access to education for underprivileged children.
- Played a central role in moral and ethical development.
- Contributed scholars, poets, and thinkers to society.
The importance of madrasa education today lies in its adaptability, balancing tradition with the digital age. The goal should be not to westernize it, but to modernize it.
Conclusion
The Madrasa Education System stands at a crossroads between tradition and transformation. Its strengths lie in its moral foundation, accessibility, and community spirit. But to truly thrive, it must embrace reforms, modern subjects, and inclusive policies.
After all, education is not about choosing between “old” and “new.” It’s about learning what’s true and useful whether it’s from a dusty manuscript or a digital screen.
So the next time someone mentions a madrasa, think beyond stereotypes. Think of centuries of knowledge, devotion, and quiet classrooms shaping lives one verse, one equation, and one hopeful student at a time.
FAQs
It’s a traditional Islamic education system focusing on both religious and, in modern times, general subjects.
More than 30,000 recognized madrasas, with many more unregistered community institutions
To improve employability, digital literacy and quality while keeping cultural roots intact.
Programs like SPQEM and SPEMM promote integration of modern subjects and infrastructure improvement.
Yes, through equivalence certificates and modernized board affiliations.